Industry Thought Leadership
5G and the Future of Networks
April, 2022On May 13th, 1897, Marconi sent the first-ever wireless communication over the open sea. The message itself held prominence as it gave a sneak peek into the adventures of a promising future. It said, “Are you ready?”
With every generation, the philosophy remains the same, making us wonder whether we are ready for the next generation. However, with the onset of 5G and its array of disruptive and transformative technologies, we pushed the envelope towards developing ultra-speed networks, massive data consumption, an interactive internet of things (IoT), and industrial automation systems.
These ultra-speed networks, enhanced machine learning and communications, as well as massive data consumption, are pushing carriers to start thinking and positioning their networks beyond 5G. This sharp transition demands to know, “Are we ready for 6G?” – which should be a transformative fusion between the physical, digital, and biological world around us. The GCC countries such as Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE (United Arab Emirates) have become pioneer in 5G networks. The 2022 world cup will bring around 1.7 million visitors to Qatar, which will be the first 5G world cup with services such as 8K live broadcasts and augmented and virtual reality.[1]
The advanced features relevant to networks will shape our evolution beyond 5G, facilitating growth opportunities and new revenue streams. Industry is taking on a vision to shape & enable access, service domains and networking in the current world. Countless opportunities will stem from these extrasensory and novel features for service innovation and business efficiencies.
Going beyond 5G networks requires a sharp transition from the traditional service model along with continuous transformations including software-centric, high-capacity network supports and enrichment of tighter coordination across multi-mode technologies.
Vision Beyond 5G
The current 5G connectivity market continues to be dominated by mobile network operators (MNOs). The business model of a communication service provider (CSP) is structured around mass provisioning with advanced investments in infrastructure and exclusive regulator-granted long-term spectrums and licenses. However, due to the advancement of 5G-powered services, there is a shift in the responsibility of delivering resources from an MNO-centric system to a dynamic mode of operation, which is becoming a necessary catalyst for deploying and operating networks of the future.
Tech Mahindra has observed these trends and therefore envisioned the overlay of the network of the future, which is a cloud-native, software-centric, fully automated, elastic, and multi-vendor ecosystem. As a result, we have further invested in software, automation tools, and frameworks for the future of networks. This unique framework of the ‘5G and beyond’ infrastructure not only addresses the elastic nature of capacity requirements, but also automates multiple network functions in deployment life cycles while bringing down costs drastically.
Similarly, our 6G network architecture vision envisages the lowest evolution expenditure that fits the network economics for carriers in their efforts to increase average revenue per subscriber. Though the architecture has been standardized as part of 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), we are also influencing our leading position towards the 6G future roadmap.
Envisioning the 6G Architecture Blueprint
We think 6G will evolve into multiple dimensions and will embrace the infrastructure, software, application, and security layers -
1. Infrastructure Layer
Every new mobile generation requires some new pioneering spectrum to make the best of the latest technology. An essential prerequisite for 6G is reframing the existing mobile communication spectrum from legacy technology to the new generation. The new pioneer spectrum blocks for 6G are expected to be at mid-bands 7 – 20 GHz (Gigahertz) for urban outdoor cells, which would enable higher capacity through extreme MIMO (Multiple input, multiple output), low bands for extreme coverage, and sub-THz (Terahertz) for peak data rates over 100 Gbps (Giga Bytes per second). In addition, new radio channels from satellite communications will be integrated with cellular bands to offer ultra-high access capacities in the radio and transport layers.
6G offers an advantage in terms of future sensing. It provides an enhanced level of coverage and the interconnection between nodes, which facilitates a multi-static sensory mesh. Furthermore, our AI-based optimization algorithms for beamforming in the radio layer can be scheduled at the cell site with efficient self-optimizing networks.
2. Open Software and Automation Layer
The software will become a cornerstone for enabling multiple access and transport layers while elastically adding capacity. Along with that, network functions will be fully automated, cloud-driven, quickly scalable, and operational, while also being monitored on a single dashboard. Our rapid investments in AI/ML (Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning) and our true potential are beginning to be utilized in 6G, along with an omnichannel coordination capability to provide a hyper-personalized experience at multiple touchpoints. This will help customize and strategize billing for industrial and consumer use cases, i.e., collaborated robots, human-centric experiences, sensory networking, gesture functionalities, etc.
We are building AI-enabled offerings which will be relevant for 6G. Proactive and predictive customer experience management (CEM) models for business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-customer (B2C) will evolve, requiring a new set of network analytics tools, real-time service assurance techniques, and ultra-fast big data processing.
3. Application Layer
It is difficult for us to capture the horizon of 6G offerings, but with the help of current 5G models, we can understand and reflect that AI/ML will play a significant role in future generations. Smartphones will play an essential role in the 6G era with new AI-enabled interfaces that would bring more convenience to consuming and controlling information. There will be a rise in gesture and voice controls adoption. VR/MR (Virtual Reality/ Mixed Reality) will become more immersive, opening new avenues for growth with human and digital transfusion. The boundaries of communication will not be limited to land and will penetrate the sea, sky, and space.
In addition, the metaverse would not just evolve into a final model but is likely to unify with the physical world. This is because the most notable aspect of 6G would be its ability to sense the environment, people, and objects. The network’s sensing ability combined with AI and machine learning will make it more cognitive. Furthermore, it will support real-time interaction between collaborative robots, allowing massive knowledge sharing along with new and larger human-machine interfaces, precise localization, and deterministic communication.
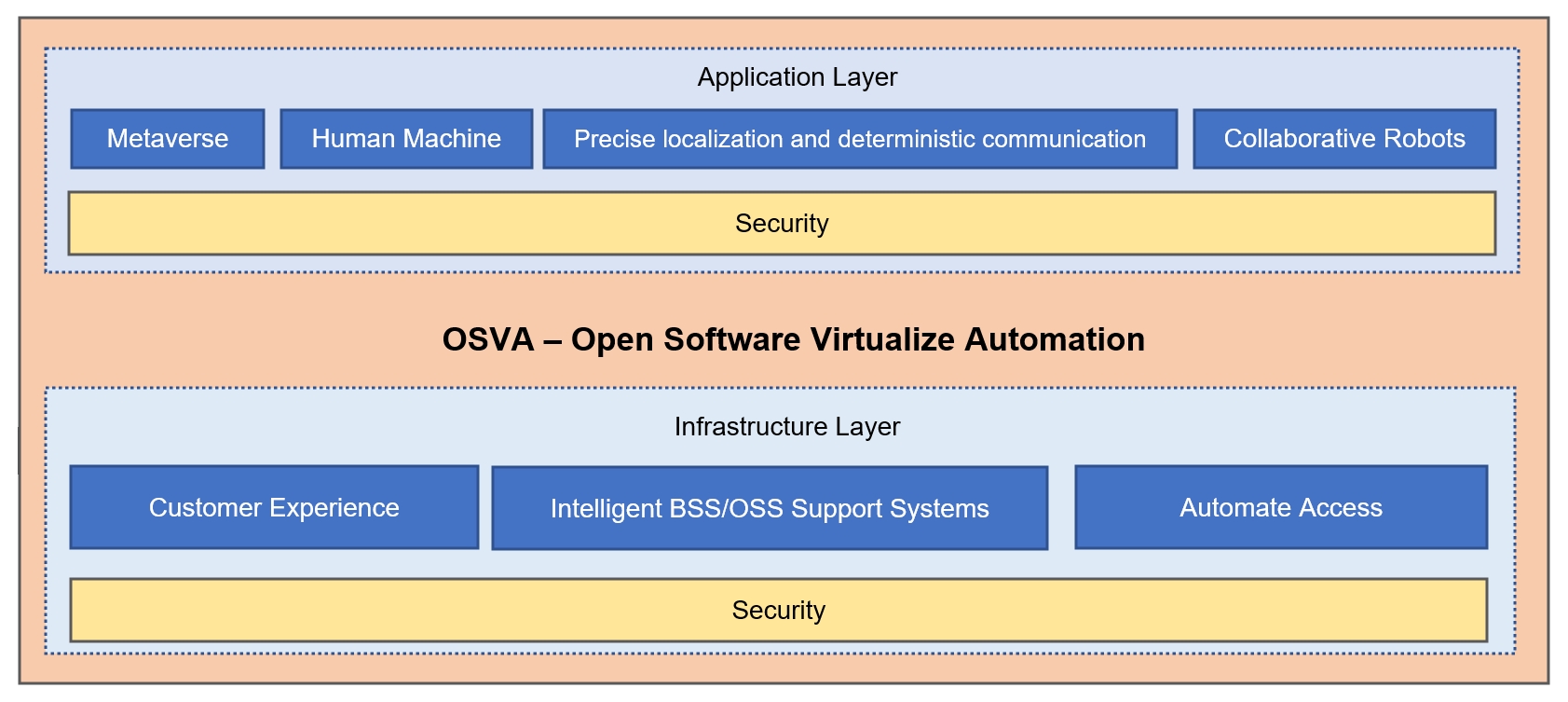
4. Security Layer
With the inferences drawn from the current 5G models and the opportunities unlocked by 6G, we can create a hyper-connected network of heterogeneous nodes. These will have a major requirement for hyper security since the data can be acquired anytime, anywhere seamlessly, even from a small object that an individual interacts with. In addition, the threat of malicious attacks will increase with 6G due to the proliferation of billions of devices and millions of subnetworks.
The dynamic nature of threats makes it imperative to deploy sturdy security mechanisms. In this regard, 6G is expected to include new dimensions in network privacy, secure communications, and resilience. Robust authentication, encryption algorithms, and methods for monitoring network security can be deployed to avoid unauthorized access to sub-network functions. Distributed AI/ML can be used as security for distinct phases of cybersecurity protection and defense in 6G.
Looking ahead: What 6G and the Future of Networks mean for us
6G technology promises to revolutionize many industries and is believed to be the foundation for realizing the full potential of the IoT. With that accomplished, we can expect these technologies to operate at a much larger scale and significantly impact the network architecture. With the lessons from the current 5G model and the opportunities unlocked by 6G, we can create a hyper-connected network of heterogeneous nodes with billions of devices and sub-networks. This is expected to include new dimensions of AI/ML technologies, robotics, sensory connectivity, and digital twins.
The next decade will witness significant developments in 6G technologies, architecture, and algorithms. Networks will benefit from remote monitoring and intelligent analytics, allowing operators to optimize operations and provide performance predictions that help businesses at every step of the way. Wireless communications in the 6G era will serve as an essential foundation for almost all industries in that economy.
The dependency of industries will grow to include their manufacturing floor, logistics supply chain, autonomous transportation, and precision agriculture. More dimensions will unfold as we progress towards the commercialization of 6G beyond 2030. As such, the time is ripe to work towards building the infrastructure and harnessing the current capabilities of 5G networks while keeping 6G on the horizon.
So, let’s get ready for 6G.

